

If spinal trigeminal nucleus is affected, this causes absence of pain on the ipsilateral side of the face as well as absence of corneal reflex. The syndrome is characterized by loss of pain and temperature sensation on the contralateral side of the body and ipsilateral side of the face. Among other causes, vertebral artery dissection due to neck manipulation/injury, Marfan's syndrome, Ehler–Danlos syndrome, and fibromuscular dysplasia may be attributed to LMS. Hypertension, diabetes, and smoking are the common risk factors. It is caused most commonly due to atherothrombotic vertebral artery occlusion, followed by posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) and medullary arteries. Wallenberg's syndrome or lateral medullary syndrome is associated with a variety of symptoms due to the involvement of the lateral segment of the medulla. The first descriptions by Wallenberg were in 1895 (clinical) and 1901 (autopsy findings). The lateral medullary syndrome (LMS) was first described in 1808 by Gaspard Vieussux. An Atypical Presentation of Left Lateral Medullary Syndrome – A Case Report.
#Pica syndrome nystagmus how to#
How to cite this URL: Renjen PN, Krishnan R, Chaudhari D, Ahmad K. How to cite this article: Renjen PN, Krishnan R, Chaudhari D, Ahmad K. Clinical presentations of brainstem infarcts may vary accordingly. Key Message: Multiple variants of Lateral Medullary Syndrome exist which need careful examination and neuroanatomical correlation. Keywords: Ataxia, Horner's, Wallenberg's syndrome

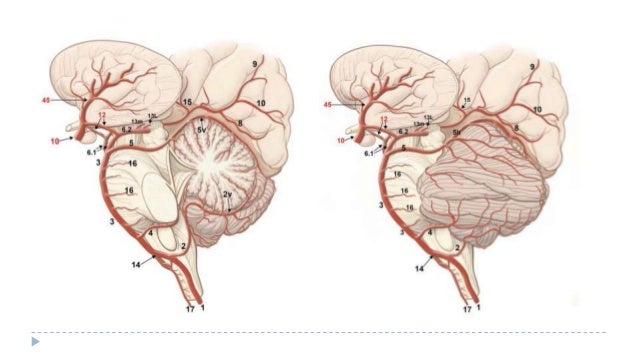
Association of these entities with Wallenberg's syndrome is atypical features in our case, which questioned the diagnosis of a simple LMS. Atypical presentation in LMS could be explained by infraction of left facial colliculus in addition to the left lateral medulla. We report a case of a 62-year-old diabetic, hypertensive male who presented with symptoms involving the left lateral dorsal medulla along with partial Horner's syndrome, left lateral rectus palsy, and left lower motor neuron–type facial palsy. The triad of Horner's syndrome, ipsilateral ataxia, and ipsilateral hyperalgesia clinically identify patients with LMS. It often results from thrombosis or emboli of the vertebral artery or posterior inferior cerebellar artery. Lateral medullary syndrome (LMS), known as Wallenberg's syndrome and posterior inferior cerebellar artery syndrome, is a rare cause of stroke.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
